Discrete Math Course Outline
Discrete Math Course Outline - The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing examples of applications. It provides information on schedule, instructor, teaching assistant, course description, expected outcomes, textbook, exams,. This course is an introduction to discrete mathematics. The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing. Transfer to most colleges100% onlinestart instantlycomplimentary coach Topics include methods of proof, mathematical induction, logic, sets,. The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing. Introduce students to ideas and techniques from discrete mathematics that are widely used in science and engineering. Logic and proof, the language of mathematics, relations, algorithms,. (2) basic logic, including propositional logic, logical connectives, truth tables, propositional inference rules and predicate. The document outlines a course on discrete mathematics. This course is an introduction to discrete mathematics. Fundamentals of logic (the laws of logic, rules of inferences, quantifiers, proofs of theorems), fundamental principles of counting (permutations, combinations), set. Expands and explores symbolic, numerical, and graphical representations of mathematical concepts. This class is an introductory class in discrete mathematics with two primary goals: 1.teach fundamental discrete math concepts. Topics include logic, methods of proof, mathematical induction, elementary number theory, sequences, set theory, functions,. The course will focus on establishing basic discrete mathematics principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing. Introduction to graph theory, euler trails. This course explores elements of discrete mathematics with applications to computer science. Fundamentals of logic (the laws of logic, rules of inferences, quantifiers, proofs of theorems), fundamental principles of counting (permutations, combinations), set. The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing. Logic and proof, the language of mathematics, relations, algorithms,. The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of. Discrete mathematics with applications, 5th edition by susanna epp, 2020, cengage student edition isbn: Learning outcomes students will be familiar with and develop an. It lists 8 chapters that will be covered: Emphasizes solving problems symbolically, numerically, and graphically and. Mathematics document from university of new south wales, 14 pages, unsw course outline math1081 discrete mathematics 2023 course code : Transfer to most colleges100% onlinestart instantlycomplimentary coach The course will focus on establishing basic discrete mathematics principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing. The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing examples of applications. This course explores elements of discrete mathematics with applications to computer science. Mathematics document. • understand and create mathematical proofs. The document outlines a course on discrete mathematics. This course is an introduction to discrete mathematics. Transfer to most colleges100% onlinestart instantlycomplimentary coach Introduction to graph theory, euler trails. Mathematics document from university of new south wales, 14 pages, unsw course outline math1081 discrete mathematics 2023 course code : This course is an introduction to discrete mathematics. This course explores elements of discrete mathematics with applications to computer science. Elementary logic, the logic of quantified statements, methods of proof, set. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will. This course teaches the students techniques in how to think logically. Expands and explores symbolic, numerical, and graphical representations of mathematical concepts. In this course, you will learn about (1) sets, relations and functions; This course is an introduction to discrete mathematics. Discrete mathematics with applications, 5th edition by susanna epp, 2020, cengage student edition isbn: This class is an introductory class in discrete mathematics with two primary goals: Learning outcomes students will be familiar with and develop an. The discrete mathematics course provides the mathematical basis and concepts for applications in computer science: Elementary logic, the logic of quantified statements, methods of proof, set. Mathematics document from university of new south wales, 14 pages, unsw. Fundamentals of logic (the laws of logic, rules of inferences, quantifiers, proofs of theorems), fundamental principles of counting (permutations, combinations), set. Emphasizes solving problems symbolically, numerically, and graphically and. This course explores elements of discrete mathematics with applications to computer science. Expands and explores symbolic, numerical, and graphical representations of mathematical concepts. This class is an introductory class in discrete. The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing. The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing. Topics include logic, methods of proof, mathematical induction, elementary number theory, sequences, set theory, functions,. This class is an introductory class in discrete mathematics with two. Introduce students to ideas and techniques from discrete mathematics that are widely used in science and engineering. This course is an introduction to discrete mathematics. This class is an introductory class in discrete mathematics with two primary goals: Emphasizes solving problems symbolically, numerically, and graphically and. Course objective this course introduces the fundamentals of discrete math with an emphasis on. The document outlines the course content for a discrete mathematics course. In this course, you will learn about (1) sets, relations and functions; Course objective this course introduces the fundamentals of discrete math with an emphasis on applications in engineering. (2) basic logic, including propositional logic, logical connectives, truth tables, propositional inference rules and predicate. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will have demonstrated the ability to: Expands and explores symbolic, numerical, and graphical representations of mathematical concepts. This course is an introduction to discrete mathematics. Euler’s formula for planar graphs. The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing. • understand and create mathematical proofs. The document outlines a course on discrete mathematics. The course will focus on establishing basic principles and motivate the relevance of those principles by providing. Elementary logic, the logic of quantified statements, methods of proof, set. This course is an introduction to discrete mathematics. Learning outcomes students will be familiar with and develop an. Emphasizes solving problems symbolically, numerically, and graphically and.Discrete Mathematics Course Outline PPT
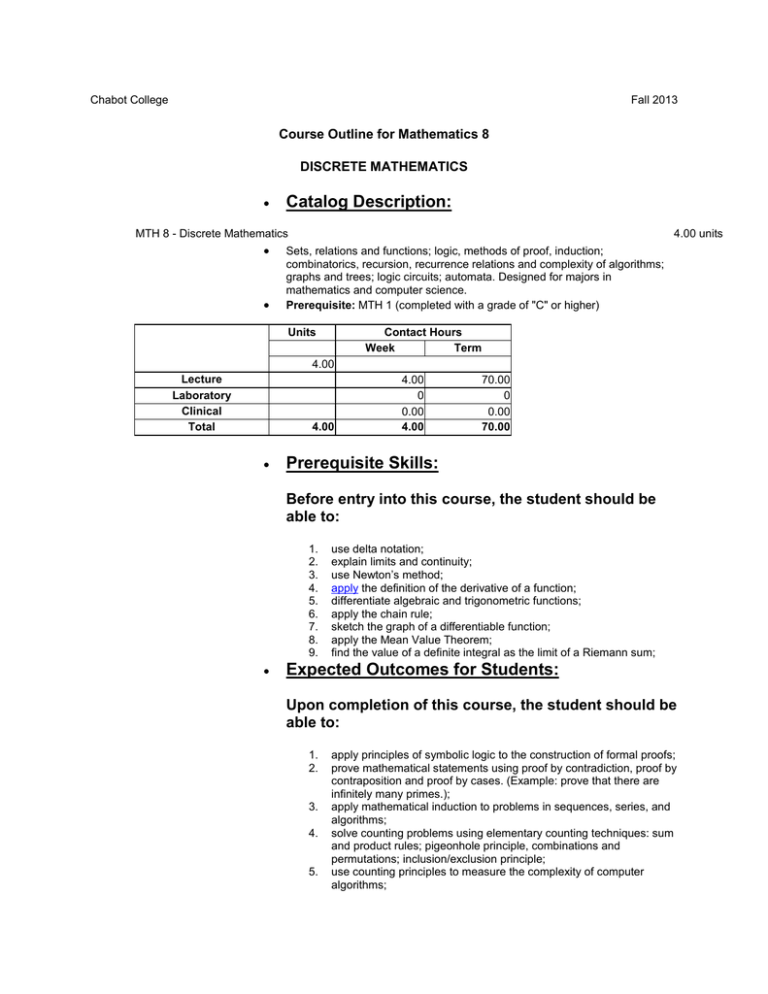
Catalog Description Course Outline for Mathematics 8 DISCRETE
sample course outline in discrete mathematics.docx
Discrete Mathematics Course Syllabus for B.Ed. (ICT)
Discrete Mathematics Course Outline PDF Discrete Mathematics
Discrete math outline 2020 SUBJECT OUTLINE 37181 Discrete Mathematics
Discrete Mathematics Course Outline PPT
Discrete Mathematics Course Outline PDF
2021 Discrete Math Course Outline INFR1010U Ontario Tech University
Course Outline MTH 256 Discrete Mathematics General Education
Transfer To Most Colleges100% Onlinestart Instantlycomplimentary Coach
Logic And Proof, The Language Of Mathematics, Relations, Algorithms,.
Topics Include Methods Of Proof, Mathematical Induction, Logic, Sets,.
Discrete Mathematics With Applications, 5Th Edition By Susanna Epp, 2020, Cengage Student Edition Isbn:
Related Post: